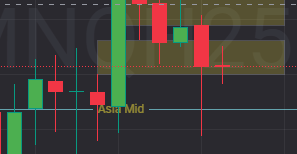
In trading, Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are an important concept that helps traders understand price inefficiencies in the market. These gaps occur when there is an imbalance between buying and selling pressure, leading to price movements that leave unfilled liquidity zones on a chart. Many traders use FVGs to identify potential entry and exit points, making them a valuable tool in technical analysis.
For beginners, understanding FVGs can seem complex at first. However, by learning how to spot these gaps, interpret their significance, and use them effectively, traders can enhance their decision-making and improve their overall strategy. This guide will break down FVGs in a simple, beginner-friendly way, helping you gain confidence in using them in your trading approach.
What is a Fair Value Gap?
A fair value gap (FVG) is a price imbalance that occurs when the market moves rapidly in one direction, creating a gap between the opening and closing prices of consecutive candles. This happens due to a sudden increase in buying or selling pressure, leaving a void where little to no trading activity has taken place.
Traders view fair value gaps as areas where price may return to fill the gap before continuing in its original direction. These gaps can act as support or resistance zones, helping traders predict potential price movements.
Understanding market inefficiencies
Market inefficiencies occur when price action does not follow a balanced or orderly movement. Fair value gaps are one type of inefficiency where supply and demand are not evenly distributed. When a large institutional order enters the market, it can push the price sharply in one direction, leaving a gap in liquidity.
These inefficiencies often get corrected as the market seeks to restore balance. Traders use this concept to anticipate price retracements, looking for opportunities to enter or exit positions based on where the gap might be filled.
Why Do Fair Value Gaps Matter in Trading?
Fair value gaps play a crucial role in technical analysis because they indicate areas where price may retrace before continuing its trend. Traders use these gaps to identify potential entry and exit points, making them a useful tool for improving trading accuracy.
When a fair value gap appears, it suggests that price moved too quickly in one direction, leaving an imbalance in the market. Many traders believe that price has a tendency to return to these gaps to “fill” the imbalance before resuming its trend. This behavior is often observed in forex, stocks, and cryptocurrency markets.
The role of liquidity and price action
Liquidity is a key factor in understanding fair value gaps. In financial markets, liquidity refers to the availability of buyers and sellers at different price levels. When a gap forms, it means there was a temporary lack of liquidity in that area, causing price to skip certain levels.
Price action traders monitor these gaps to anticipate where liquidity might be reintroduced. When price revisits a fair value gap, traders watch for signs of reversal or continuation, using it as a reference point for trade execution. This approach helps traders make informed decisions based on past market behaviour.
How to Identify Fair Value Gaps on a Chart
Identifying fair value gaps requires analyzing price charts to spot areas where price moved too quickly, leaving an imbalance. These gaps typically appear in strong trending markets and can be found on different timeframes, depending on a trader’s strategy.
A fair value gap is usually identified when a three-candle formation occurs:
- The first candle moves strongly in one direction.
- The second candle continues the move, creating a gap between its open and the previous candle’s close.
- The third candle does not completely fill the gap, confirming the imbalance.
Traders often mark these areas on their charts as potential zones where price might return before resuming its trend.
Key indicators and tools for spotting FVGs
While fair value gaps can be identified manually by analyzing candlestick patterns, some traders use tools to simplify the process. Common methods include:
- Price action analysis – Observing candlestick formations and large impulsive moves.
- Volume indicators – Checking for low trading activity in gap areas.
- Moving averages – Using moving averages to confirm trend direction and potential retracement levels.
- Custom indicators – Some platforms offer FVG indicators that automatically highlight gaps on charts.
By combining these tools, traders can improve their ability to spot and utilize fair value gaps effectively in their trading strategies.
Trading Strategies Using Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps can be used in various trading strategies to improve entry and exit points. Since these gaps represent price inefficiencies, traders look for opportunities where price is likely to return to these levels before continuing its trend.
Some traders use fair value gaps as support or resistance zones. When price revisits an unfilled gap, it often reacts by either reversing or continuing in its original direction. Understanding how to incorporate fair value gaps into a trading plan can help traders make more informed decisions.
How traders use FVGs for entries and exits
There are several ways traders use fair value gaps in their strategies:
- Entry confirmation – Traders wait for price to return to a fair value gap and look for confirmation signals, such as candlestick patterns or volume changes, before entering a trade.
- Trend continuation trades – In a strong trend, price may retrace to fill a fair value gap before resuming its movement. Traders use this as an opportunity to enter in the direction of the trend.
- Reversal trades – If price fills a fair value gap and shows signs of rejection, traders may take a counter-trend trade expecting a reversal.
- Stop-loss placement – Some traders place stop-loss levels just outside a fair value gap to minimize risk in case price moves unexpectedly.
By using fair value gaps alongside other technical indicators, traders can refine their strategies and improve their overall trading performance.
Common Mistakes When Trading Fair Value Gaps
While fair value gaps can be a useful tool in trading, misinterpreting them can lead to poor decisions. Beginners often make mistakes when identifying or using these gaps, which can result in unnecessary losses. Understanding these common errors can help traders avoid pitfalls and improve their trading performance.
How to avoid false signals and misinterpretations
Some of the most common mistakes when trading fair value gaps include:
- Ignoring market context – Fair value gaps should not be traded in isolation. It’s important to consider overall market trends, support and resistance levels, and key technical indicators before making a decision.
- Entering trades without confirmation – Just because price returns to a fair value gap does not mean it will always reverse or continue in the expected direction. Waiting for confirmation signals, such as candlestick patterns or volume changes, can help improve trade accuracy.
- Trading every fair value gap – Not all gaps are significant. Traders should focus on gaps that align with strong trends and key price levels to avoid unnecessary trades.
- Using fair value gaps on the wrong timeframe – Different timeframes can show different fair value gaps. Short-term traders may focus on intraday gaps, while long-term traders look at gaps on higher timeframes for stronger signals.
- Neglecting risk management – Even with a high-probability setup, risk management is essential. Setting stop-loss levels and using proper position sizing can prevent large losses if the trade does not go as expected.
By avoiding these mistakes and combining fair value gaps with other technical analysis tools, traders can make more informed decisions and increase their chances of success.
Conclusion
Fair value gaps are a valuable tool for traders looking to identify price inefficiencies and improve their trading strategies. By understanding how these gaps form and how price tends to react to them, traders can make more informed decisions about entries and exits.
While fair value gaps can provide high-probability trade setups, they should not be used in isolation. Combining them with other technical analysis tools, such as support and resistance levels, trend indicators, and volume analysis, can help increase accuracy and reduce risk.
For beginners, mastering fair value gaps takes practice. Observing how price interacts with these gaps in real-time and backtesting strategies can help traders develop confidence in using them effectively. With proper risk management and a well-structured approach, fair value gaps can become a powerful addition to a trader’s toolkit.